Exciton Seminar: Prof Douglas MacFarlane
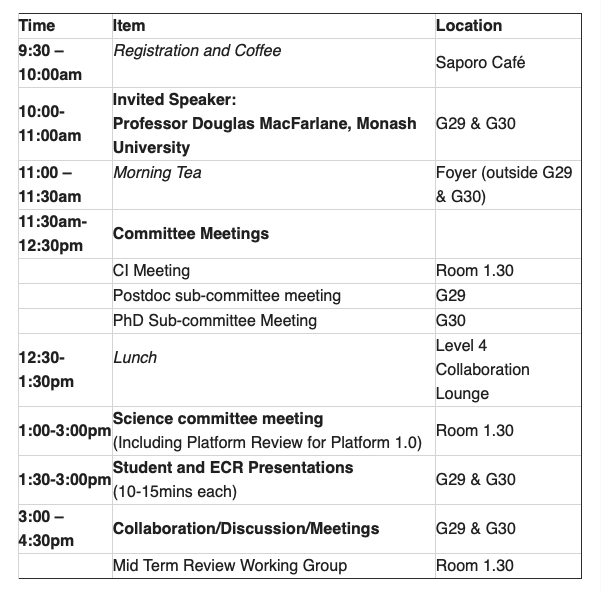
The next Exciton Seminar on Friday 4 October at Monash University. This will feature guest speaker Professor Douglas MacFarlane from the School of Chemistry at Monash. We will also hold ECR and PhD presentations and various meetings.
Please register by Monday 30 September for catering purposes.
The event is for Exciton Science members (including CIs, PIs, AIs, researchers and students.)
ABSTRACT
Chemical Energy Storage Applications of Ionic Liquids – from Hydrogen to Ammonia
Doug MacFarlane, Australian Centre for Electromaterials Science, School of Chemistry, Monash University, Victoria, Australia
E-mail: doug.macfarlane@monash.edu
Efficient production of ammonia from renewable energy represents an important technology for future means of global transportation of renewable energy from remote land and marine areas where it can be generated inexpensively at massive scale. Ammonia is readily transportable and can be cracked into hydrogen at point of use or used directly as a fuel in gas turbines and large vehicles. However, the direct nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR), coupled with the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), are of relatively low efficiency under ambient conditions compared to other energy storage mechanisms and this is currently limiting the technology. The materials being developed for use as electro-catalytic materials for these processes as well as media will be overviewed in this talk.1
One of the reasons for the low efficiency in the NRR process2 is the very poor solubility of N2 in many electrochemical solvents. Fortunately, some ionic liquids offer considerably higher nitrogen solubility, up to 20 times or more than in water, and this has allowed us to demonstrate breakthrough levels of selectivity in this reaction.3, 4 Blending these ionic liquids with high solubility aprotic solvents overcomes the high viscosity of the ionic liquid and improves the rate of the processes.5 We will discuss recent progress in this area based on development of new ionic liquids and exploring their mixtures with various solvents.6
References
SEMINAR SCHEDULE